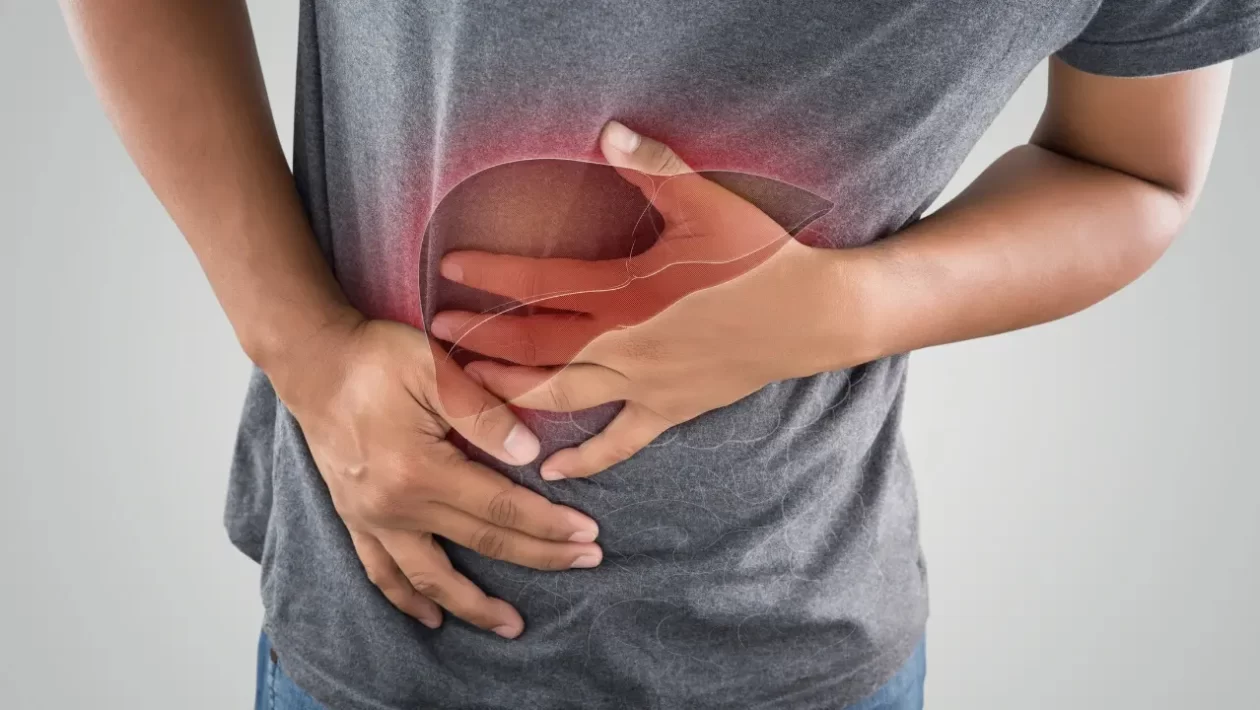
Hepatitis is a liver disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition characterized by inflammation of the liver, which can lead to various complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the different types of hepatitis, their causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Types of Hepatitis
There are several types of hepatitis, including hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, and hepatitis E. Each type is caused by a different virus, and they vary in their modes of transmission, severity, and long-term effects.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is usually transmitted through contaminated food or water. It is an acute infection that does not lead to chronic liver disease. Symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Vaccination is available to prevent hepatitis A.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is primarily transmitted through contact with infected blood, unprotected sex, or from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. It can lead to chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Vaccination is available and is highly effective in preventing hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is transmitted through contact with infected blood, primarily through sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia. It can lead to chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing long-term complications.
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D only occurs in individuals who are already infected with hepatitis B. It is transmitted through contact with infected blood or sexual contact. Hepatitis D can accelerate the progression of liver disease and increase the risk of severe complications.
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is usually transmitted through contaminated water or food, similar to hepatitis A. It is more prevalent in developing countries with inadequate sanitation. While most cases resolve on their own, pregnant women are at higher risk of severe complications.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of hepatitis include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and nausea. Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests that detect specific hepatitis viruses and assess liver function.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hepatitis depends on the type and severity of the infection. Acute hepatitis may not require specific treatment, as the immune system can clear the infection on its own. Chronic hepatitis may require antiviral medications to suppress the virus and reduce liver inflammation. In some cases, liver transplantation may be necessary for end-stage liver disease.
Preventive Measures
Preventing hepatitis involves various strategies, including practicing good hygiene, safe sexual practices, and avoiding sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia. Vaccination is available for hepatitis A and B, and it is recommended for at-risk individuals.
Conclusion
Hepatitis is a significant global health concern, affecting millions of individuals and causing substantial morbidity and mortality. Understanding the different types of hepatitis, their modes of transmission, and available prevention measures is crucial for reducing the burden of this liver disease. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and adopting preventive measures can help protect liver health and prevent long-term complications associated with hepatitis. By raising awareness and promoting preventive practices, we can strive towards a world with reduced incidence and impact of hepatitis on individuals and communities.