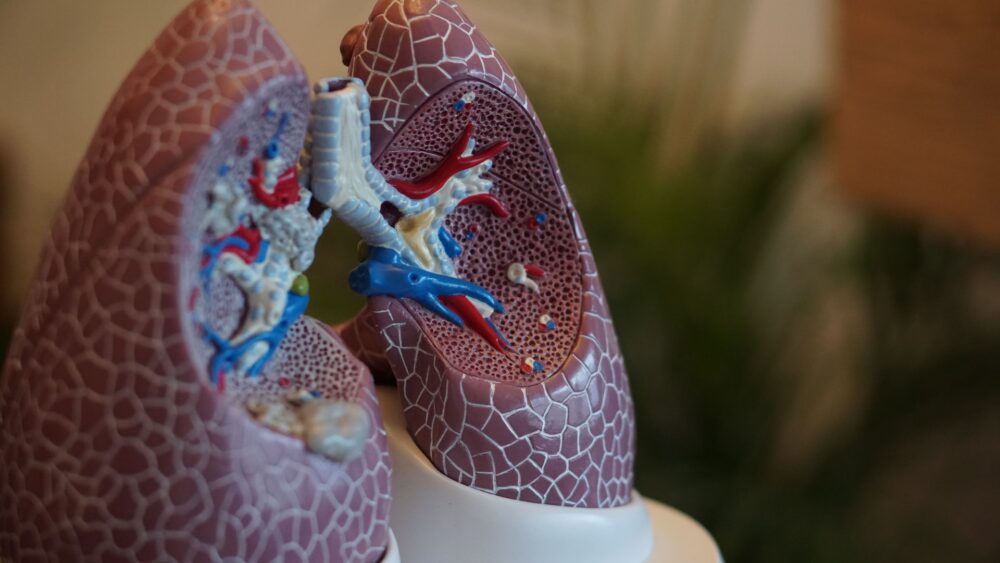
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs, which can range in seriousness from mild to life-threatening. Pneumonia is a serious condition in particularly infants, children, people over 65 and people with other diseases, and those with weakened immune systems.
Pneumonia normally starts with a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection, leading to inflammation in the air sacs in your lungs, called alveoli. The alveoli fill with fluid or pus causing cough with phlegm and difficulty breathing.
There are more than 30 different causes of pneumonia, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and airborne irritants.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
The germs that cause pneumonia are contagious. You can encounter the germs that cause pneumonia in the most common of places, and the environment you frequent on a daily basis.
Both viral and bacterial pneumonia can spread to others through inhalation of airborne droplets from a sneeze or cough. Generally, viral pneumonia is more likely to spread from person to person than pneumonia caused by bacteria or fungus. Fungal pneumonia doesn’t spread person to person, however, you can contract it from the environment.
Some types of pneumonia, like Legionnaires’ disease, spread only in certain environments. Legionnaires’ disease, caused by the bacteria Legionella pneumophila, may only pose a threat when exposed to a contaminated air conditioning system.
Pneumonia Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of pneumonia can range from mild to severe, to life-threatening. Signs and symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Cough that may produce phlegm(mucus)
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
- Fever
- Sweating or chills
- Feeling tiredness or fatigue
- Fast breathing and/or shortness of breath
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Confusion or delirium, especially in older adults
Newborns and children under 5 years old may experience fast breathing or wheezing. Infants can also vomit, have a fever and cough or have trouble drinking or eating. They can also exhibit no symptoms or sign of infection.
With older adults, they can have milder symptoms. Pneumonia can catch anyone, so if you or your child is experiencing these symptoms, check in with your healthcare provider.
Pneumonia in Children
Pneumonia is quite a common condition in infants and children. Researchers estimate there are 120 million cases of pediatric pneumonia worldwide each year. In children, pneumonia is usually due to a virus.
The causes of childhood pneumonia can vary by age. Pneumonia due to respiratory viruses, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae is more common in children under 5 years old. Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae, on the other hand, is frequently observed in children between the ages of 5 and 13.
Symptoms of pneumonia in children include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Coughing
- Fever
- Not eating properly
- Lack of energy
- Irritability
What are the Causes of Pneumonia?
The most common causes of pneumonia cases are bacteria and viruses. Pneumonia is classified according to the types of germs that cause it and where you got the infection.
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is mainly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and is the most common in adults. This type of pneumonia usually affects one area of the lung and is referred to as lobar pneumonia. Bacterial pneumonia can occur on its own or may follow a cold or the flu (influenza).
Types of bacteria that cause pneumonia include Legionella pneumophila, the cause of Legionnaires’ disease, or Legionellosis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib).
Viral Pneumonia
Viruses are responsible for about one-third of all pneumonias, and they’re the most common cause of pneumonia in children younger than age 5. Viral pneumonia is usually mild and tends to clear up in about one to three weeks. However, in some cases, it can become serious. For example, Coronavirus (COVID-19) may cause pneumonia, which can become severe.
Viral pneumonia is caused by respiratory viruses such as influenza (flu), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinoviruses (common cold).
Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is generally caused by fungi from soil or bird droppings. Fungal pneumonia is most common in people with chronic health problems or weakened immune systems.
Three types of fungi living in soil known to cause pneumonia include Coccidioides immitis and Coccidiodes posadasii, Histoplasma capsulatum, and Cryptococcus. These can also affect people who have inhaled large doses of the organisms.
What Health Complications Can Pneumonia Lead to?
A case of pneumonia can cause complications, especially in people with weakened immune systems or chronic conditions. If left untreated, pneumonia can become severe. If you have pre-existing health conditions, pneumonia could make them worse. For some people, pneumonia increases their risk of having a heart attack.
Bacteria from pneumonia infection can enter the bloodstream from your lungs can spread the infection to other organs, which can lead to dangerously low blood pressure, septic shock, and in some cases, organ failure. Other complications pneumonia can pose includes lung abscess, impaired breathing, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and fluid accumulation around the lungs, known as pleural effusion.
If you are displaying any similar symptoms, that persist or worsen, talk to your doctor. In order to confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific cause of the illness, you may get a chest X-ray as well as a blood test, depending on your medical history and physical exam, if your doctor suspects that you have pneumonia.