Osteoporosis is a prevalent and often silent disease that weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. Despite its common occurrence, many individuals are unaware of its impact until a fracture or bone breakage occurs. In this article, we will delve into the world of osteoporosis, exploring its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What is Osteoporosis?
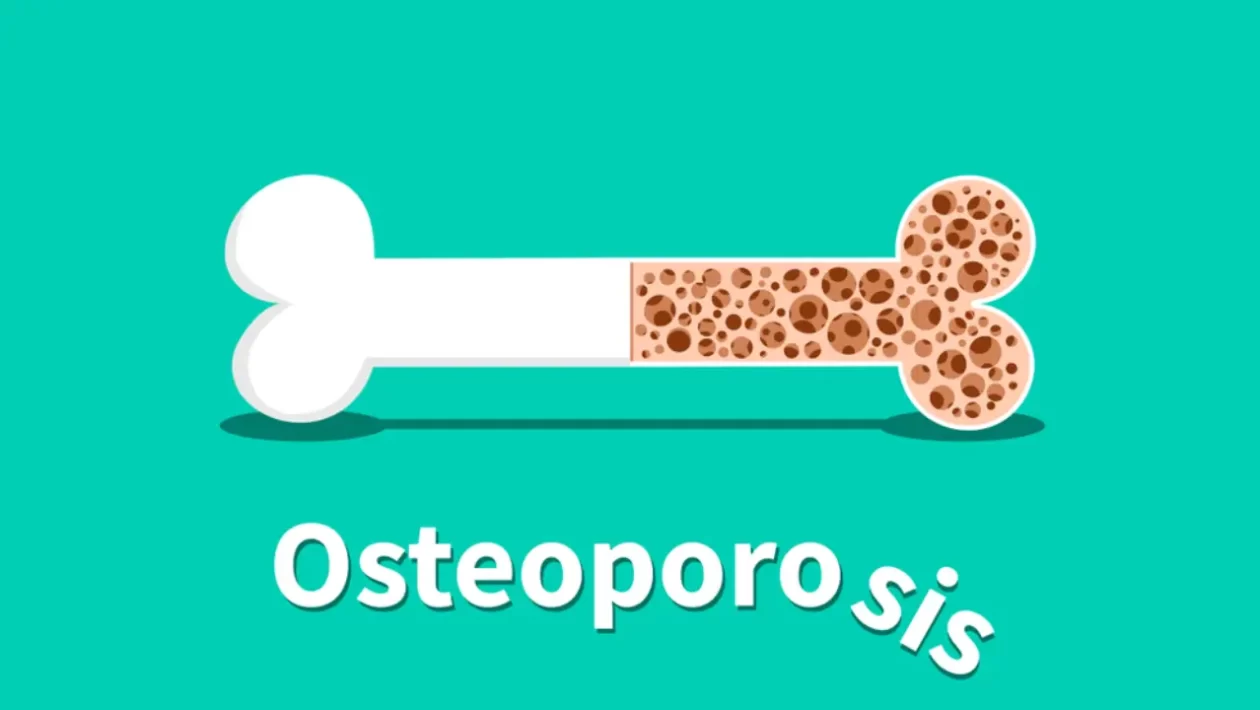
Osteoporosis is a chronic condition characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue. It occurs when the body fails to produce sufficient new bone or when existing bone is reabsorbed faster than it is replaced. This imbalance leads to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Understanding Bone Health
To understand osteoporosis better, it is essential to grasp the basics of bone health. Bones are living tissues that constantly undergo a process called remodeling, involving the removal of old bone tissue and the formation of new bone. This dynamic process helps maintain bone strength and structure.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Age, gender, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, sedentary lifestyle, certain medical conditions, and medications can all influence the risk of osteoporosis. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps toward prevention.
Recognizing Symptoms
Osteoporosis is often referred to as a silent disease because it does not typically present noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. However, there may be warning signs such as loss of height, gradual curvature of the spine, and chronic back pain. Recognizing these symptoms can prompt individuals to seek early detection and treatment.
Diagnostic Methods
Bone density testing, specifically through dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), is the gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis. This painless and non-invasive test measures bone mineral density, providing valuable information about an individual’s bone health and fracture risk.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for osteoporosis aims to prevent further bone loss, improve bone density, and reduce the risk of fractures. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption play a crucial role. Additionally, healthcare providers may recommend medications to help strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention is key when it comes to osteoporosis. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits from an early age can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. This includes ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercises, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining healthy body weight.
Conclusion:
Osteoporosis is a widespread condition that affects millions of people worldwide, primarily women and the elderly. By increasing awareness about osteoporosis, its risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their bone health. Regular bone density screenings, adopting a bone-friendly lifestyle, and seeking appropriate treatment can help individuals maintain strong and healthy bones, ensuring a better quality of life for years to come.